World Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Cereal Production is 33%
Agronomy Journal 91:357
| Facts: |
- N has no odor, is tasteless, and colorless.
- Nitrogen gas (N2) makes up 78.1% of the
Earth's atmosphere
- Atmosphere contains an estimated 4,000 trillion
tons of N2
- Nitrogen is not a metal.
- Nitrogen gas is inert. Some soil bacteria can 'fix'
nitrogen into a form that plants and animals can use to make amino acids
and proteins.
- French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisier named
nitrogen azote, meaning without life.
- Nitrogen was sometimes referred to as 'burnt' or 'dephlogisticated'
air.
- Nitrogen compounds are found in foods, fertilizers,
poisons, and explosives.
- Nitrogen is responsible for the orange-red,
blue-green, blue-violet, and deep violet colors of the aurora.
- One way to prepare nitrogen gas is by liquefaction
and fractional distillation from the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen has a valence of 3 or 5.
- Discovery:
Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772
- Fifth most abundant element in the universe
Atomic Number 7 (more)
Periodic
Table
Atomic Mass 14.0067

Commercial fertilizer is responsible for 40 to 60% of the worlds food
production (Roberts, 2009)
Roberts, T.L. 2009. The role of fertilizer in
growing the world's food. Better Crops: 93:12-15)
|
Physical properties of Nitrogen |
 |
Boiling Point at 1 atm
Freezing Point at 1 atm
Density of the gas at 21.1 C and 1 atm
|
-195.8 C
-209.9 C
1.153 kg/m3
|

|
| Uses of Nitrogen |
 |
Nitrogen finds use in diverse
commercial applications, including:
|
|
|
Chemical Processing ... to inert vessels and oxygen-sensitive chemicals,
creating an oxygen-deficient
environment that reduces safety hazards; to propelliquids through pipelines; and to manufacture ammonia.
|
|
|
|
Food ... to extend shelf-life in packaged foods by
preventing spoilage from oxidation, mold growth,
moisture migration and insect infestation; to rapidly
freeze; and to refrigerate perishables during transport.
|
|
|
|
Petroleum Recovery and Refining ... to improve
recovery and maintain pressure in oil and gas
reservoirs; to blanket storage tanks and product
loading/unloading; to purge pipelines; and to strip
volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from waste streams or
to cool vent streams. Controlling VOC emissions helps
refiners comply with U.S. Clean Air Act requirements.
|
|
|
|
Metal Production and
Fabrication ... to protect metals such as steel,
copper and aluminum during annealing, carburizing and
sintering operations in high temperature furnaces; to
cool extrusion dies; and to shrink fit metal parts;
utilized as a purge gas with stainless steel tube
welding. Also used to support plasma cutting.
|
|
|
|
Electronics ... to prevent oxidation in the
manufacture of semiconductors and printed circuits; and
to enhance solvent recovery systems by eliminating the
use of chlorofluorocarbons for cleanup.
|
|
|
|
Glass Manufacturing ... to cool furnace electrodes
and prevent oxidation during manufacturing; and to lower
air temperatures for optimum cooling rates.
|
|
|
|
Research and Health Services ... to
freeze and preserve blood, tissue, semen and other
biological specimens; to freeze and destroy diseased
tissue in cryosurgery and dermatology; and to pre-cool
or insulate Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), conserving
the more costly helium.
|
|
|
|
Construction ... to suppress the pour
temperature of concrete mixtures, inhibiting the
formation of cracks; and to stabilize the ground as in
the restoration of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. |
|

|
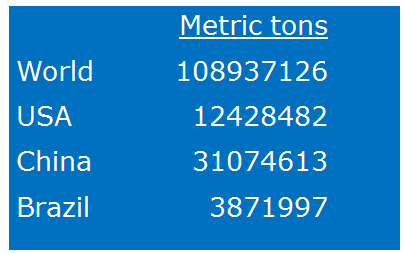
Fertilizer Consumed, 2014, FAOSTAT, 2014
 |
|
|
|
 Nitrogen
Facts
Nitrogen
Facts


